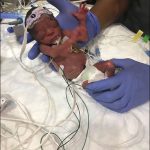
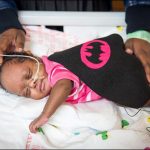
When Blessing Quartey was born, she was only 24 weeks old and weighed just 1.8 pounds.
To help boost her growth, Blessing’s mother, Eva Nehikare, agreed to enter her daughter into an ongoing study at Texas Children’s Pavilion for Women focused on the benefits of an exclusive human milk-based diet in extremely low-birth-weight babies. Five months later, Eva is thankful she did.
“Shortly after she got into the study, you could see her becoming more muscular and full,” Eva said. “When you look at her now, you would never know she is a preemie.”
Today, Blessing weighs 8 pounds. She is steadily gaining weight and growing, and was discharged from the hospital just before the holidays.
Dr. Amy Hair, neonatologist and director of the neonatal nutrition program at Texas Children’s Hospital, is leading the study Blessing is in and said the infant’s outcome isn’t uncommon.
“We’ve known for a while that a human milk-based diet is best for low-birth-weight babies,” Hair said, noting that Texas Children’s was the first pediatric hospital to adopt an exclusive human milk-based diet in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) in 2009. “Now, we have a study and outcomes to back us up.”
Hair recently published some of the study’s outcomes in the BMJ, one of the world’s oldest and most highly revered peer-reviewed medical journals.
Specifically, the study looked at the benefits of an exclusive human milk-based diet in 51 premature infants. It compared post-discharge growth, obesity and metabolic outcomes of appropriate for gestational age (AGA) premature infants versus small for gestational age (SGA) premature infants who were fed an exclusive human milk-based diet in the NICU.
The first to look at long-term post-discharge growth of this population, the study found that at 2-years-old SGA premature infants who received an exclusive human milk-based diet showed greater catch-up growth without increased obesity or elevated insulin resistance compared with AGA premature infants. These findings suggest an exclusive human milk-based diet in the NICU could lead to favorable metabolic outcomes in SGA children.
“Historically, we have overfed premature babies with either formula or cow-based fortifier, which has led to a higher risk of heart disease and metabolic problems as young adults,” Hair said. “This study proves that feeding with human milk and human milk fortifier, low-birth-weight babies grow in a healthier manner. The study also challenges the current belief that SGA babies will never catch up to their counterparts. We are seeing that they are.”
Hair said the next paper to come out about the study will focus on participants’ neurodevelopment. She added that she and her partners have seen positive results and that the families involved are extremely pleased and more than willing to participate and come in for follow-up visits.
“I am so thankful for all of the care my daughter and I received at the Pavilion for Women,” Eva said. “The opportunity for us to be a part of this was an honor.”