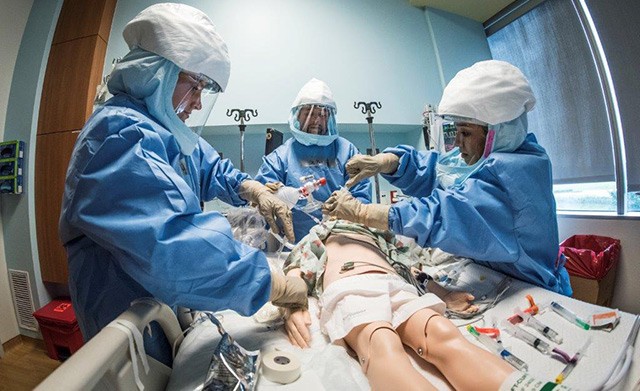
 Texas Children’s recently participated in a large-scale exercise focusing on the transport of an Ebola-positive pediatric patient from a facility in The Woodlands to Texas Children’s Special Isolation Unit at Texas Children’s Hospital West Campus.
Texas Children’s recently participated in a large-scale exercise focusing on the transport of an Ebola-positive pediatric patient from a facility in The Woodlands to Texas Children’s Special Isolation Unit at Texas Children’s Hospital West Campus.
As the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention-designated pediatric Ebola treatment center for the southwest region, Texas Children’s was chosen to be a part of the exercise organized by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to test the nationwide ability to move patients with highly infectious diseases safely and securely to regional treatment centers.
“Providing safe, high-level care for patients with highly infectious special pathogens, such as the Ebola virus, requires an incredible amount of training and preparation,” said Dr. Amy Arrington, medical director of Texas Children’s Special Isolation Unit. “We do this exceeding well at Texas Children’s Hospital, with a state-of-the-art Special Isolation Unit and incredible team of volunteer health care workers who train regularly to care for these patients. But it is also critical to practice coordinating the transport of these patients as a medical community, between health care facilities.”
More than 50 organizations throughout the nation participated in the exercise, including the Department of State, Department of Transportation, the Regional Ebola Treatment Centers, local and state health and emergency management agencies, hospitals, airport authorities, and non-government organizations.
The exercise focused on moving seven people acting as patients with Ebola symptoms in different regions of the country. At each health care facility, clinical workers simulated the collection and shipment of samples for diagnostic tests to state laboratories, which in turn practiced running the necessary laboratory tests to diagnose the patients with Ebola.
As part of the exercise, each patient received a positive diagnosis. Using appropriate isolation techniques and personal protective equipment, health care workers then took steps to have six of the patients transported by air to designated Regional Ebola Treatment Centers. These patients were placed into mobile biocontainment units for these flights. The pediatric patient was placed into protective equipment and transported by ground ambulance.
“Saving lives during crises requires preparation and training,” said Dr. Robert Kadlec, Health and Human Services Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response. “A tremendous amount of coordination, synchronization, and skill is needed to move patients with highly infectious diseases safely. We have to protect the patients and the health care workers caring for those patients. This type of exercise helps ensure that everyone involved is ready for that level of complexity.”

